Engine analysis

This service monitors engine and lubricant conditions to detect premature wear and contamination
Description
Monitoring engine and lubricant conditions help you detect problems and contamination before they result in excessive wear and failure. This analysis is applicable to spark or compression engines in virtually all types of mobile and stationary equipment, and helps to support an Optimized Drain Interval (ODI) program.
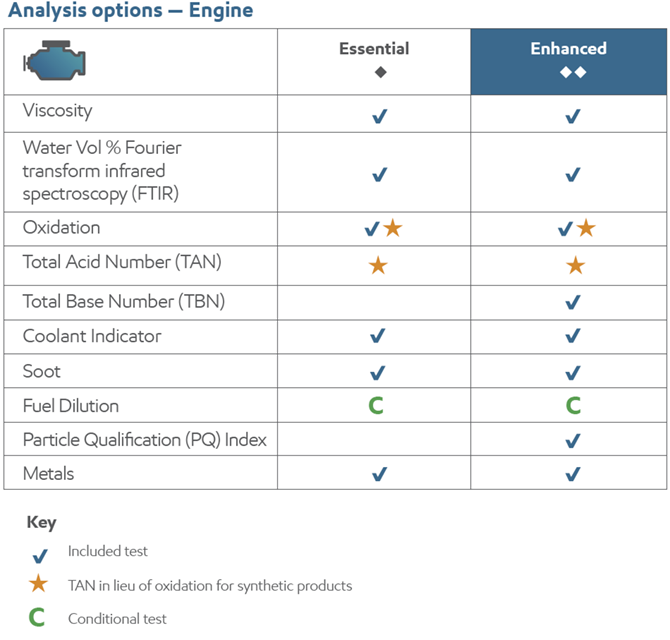
| Test | Purpose | Importance of test |
|---|---|---|
| Coolant Indicator | To determine the level of sodium, potassium and boron in the engine oil | Indicative of a coolant leak into the engine via a worn head gasket, cracked block or head |
| Fuel Dilution | To measure the amount of unburned fuel that goes to the crankcase | The presence of fuel in the crankcase reduces oil viscosity and weakens detergency. Excessive amounts may indicate potential mechanical problems |
| Metals | To determine the presence and levels of metallic content in the oil, including contaminants and wear particles | The level of metals helps determine if equipment components are wearing or if harmful contamination is entering the oil. The level of metals that are part of the additive chemistry are also reported |
| Oxidation | To determine the level of lubricant oxidation and deterioration |
Oxidation can mean:
|
| Particle Qualification (PQ) Index | To determine ferrous metal fatigue failures and metal-to-metal contact not usually detectable with current spectrographic analysis |
PQ Index can detect at an early stage:
|
| Soot | To determine the soot content in an oil by percentage weight |
Excessive soot contamination may mean:
|
| Total Acid Number (TAN) | To measure acidic oil oxidation by-products | An elevated Total Acid Number may indicate increased oil acidity resulting from increased oil oxidation |
| Total Base Number (TBN) | To determine the reserve alkalinity of the oil used to neutralize the formation of acids |
A decrease in Total Base Number may be indicative of:
|
| Viscosity | To determine the oil’s resistance to flow |
|
| Water | To detect presence of water contamination | Water contamination may cause severe corrosion and subsequent wear, poor oil film thickness or hydrogen embrittlement |
